HTTP Scaling for Ingress-Based Applications
This guide demonstrates how to scale applications exposed through Kubernetes Ingress based on incoming HTTP traffic. You’ll deploy a sample application with an Ingress resource, configure a ScaledObject, and see how Kedify automatically manages traffic routing for efficient load-based scaling—including scale-to-zero when there’s no demand.
Architecture Overview
Section titled “Architecture Overview”For applications exposed via Ingress, Kedify automatically rewires traffic using its autowiring feature. When using the kedify-http scaler, traffic flows through:
Ingress -> kedify-proxy -> Service -> Deployment
The kedify-proxy intercepts traffic, collects metrics, and enables informed scaling decisions. When traffic increases, Kedify scales your application up; when traffic decreases, it scales down—even to zero if configured.
Prerequisites
Section titled “Prerequisites”- A running Kubernetes cluster (local or cloud-based).
- The
kubectlcommand line utility installed and accessible. - Connect your cluster in the Kedify Dashboard.
- If you do not have a connected cluster, you can find more information in the installation documentation.
- Install hey to send load to a web application.
Step 1: Deploy Application and Ingress
Section titled “Step 1: Deploy Application and Ingress”Deploy the following application and Ingress to your cluster:
kubectl apply -f application.yamlThe whole application YAML:
apiVersion: apps/v1kind: Deploymentmetadata: name: applicationspec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: application template: metadata: labels: app: application spec: containers: - name: application image: ghcr.io/kedify/sample-http-server:latest imagePullPolicy: Always ports: - name: http containerPort: 8080 protocol: TCP env: - name: RESPONSE_DELAY value: '0.3'---apiVersion: v1kind: Servicemetadata: name: application-servicespec: ports: - name: http protocol: TCP port: 8080 targetPort: http selector: app: application type: ClusterIP---apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1kind: Ingressmetadata: name: application-ingressspec: rules: - host: application.keda http: paths: - path: / pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: application-service port: number: 8080Deployment: Defines a simple Go-based HTTP server that listens for requests, responds with a configurable delay, and exposes metrics.Service: Routes traffic to the application pods within the cluster.Ingress: Exposes the application outside the cluster using the hostnameapplication.keda.
Step 2: Apply ScaledObject to Autoscale
Section titled “Step 2: Apply ScaledObject to Autoscale”Now, apply the following ScaledObject:
kubectl apply -f scaledobject.yamlThe ScaledObject YAML:
kind: ScaledObjectapiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1metadata: name: applicationspec: scaleTargetRef: apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment name: application cooldownPeriod: 5 minReplicaCount: 0 maxReplicaCount: 10 fallback: failureThreshold: 2 replicas: 1 advanced: restoreToOriginalReplicaCount: true horizontalPodAutoscalerConfig: behavior: scaleDown: stabilizationWindowSeconds: 5 triggers: - type: kedify-http metadata: hosts: application.keda pathPrefixes: / service: application-service port: '8080' scalingMetric: requestRate targetValue: '1000' granularity: 1s window: 10s trafficAutowire: ingresstype(kedify-http): Specifies the Kedify HTTP scaler for monitoring HTTP traffic.metadata.hosts(application.keda): The hostname to monitor for traffic.metadata.pathPrefixes(/): The path prefix to monitor.metadata.service(application-service): The Kubernetes Service associated with the application.metadata.port(8080): The port on the service to monitor.metadata.scalingMetric(requestRate): The metric used for scaling decisions.metadata.targetValue(1000): Target request rate; KEDA scales out when traffic meets or exceeds this value.metadata.granularity(1s): The time unit for the targetValue (requests per second).metadata.window(10s): Granularity at which the request rate is measured.metadata.trafficAutowire(ingress): Enables Kedify’s ingress autowiring feature.
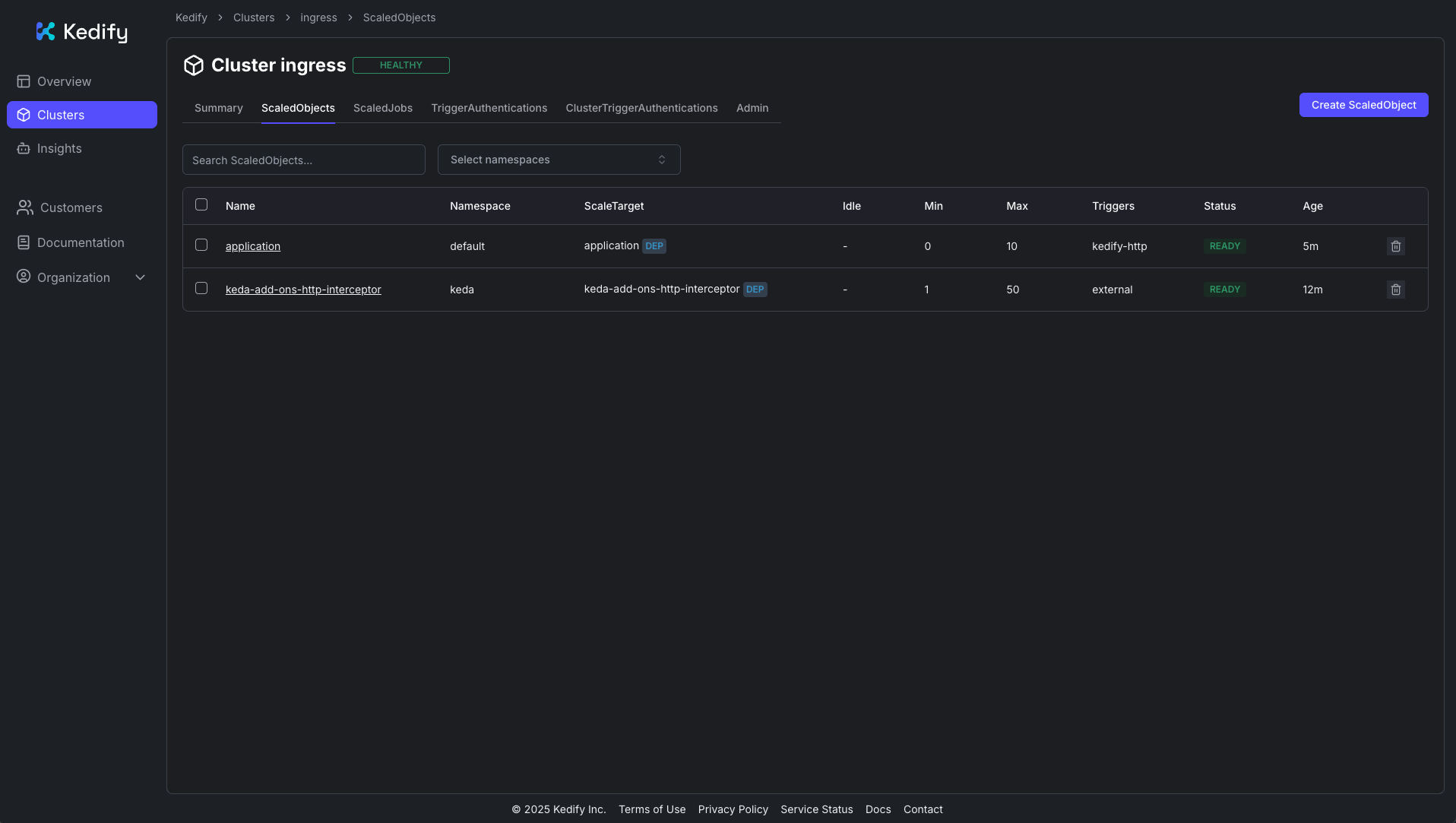
You should see the ScaledObject in the Kedify Dashboard:
Step 3: Test Autoscaling
Section titled “Step 3: Test Autoscaling”First, let’s verify that the application responds to requests:
# If testing locally with k3d (if testing on a remote cluster, use the Ingress IP or domain)curl -I -H "Host: application.keda" http://localhost:9080If everything is working, you should see a successful HTTP response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OKcontent-type: text/htmldate: Wed, 16 Apr 2025 11:32:30 GMTcontent-length: 320x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 302server: envoyNow, let’s test with higher load:
# If testing locally with k3d (if testing on a remote cluster, use the Ingress IP or domain)hey -n 10000 -c 150 -host "application.keda" http://localhost:9080After sending the load, you’ll see a response time histogram in the terminal:
Response time histogram: 0.301 [1] | 0.498 [9749] |■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■ 0.695 [0] | 0.892 [0] | 1.090 [0] | 1.287 [0] | 1.484 [0] | 1.681 [53] | 1.878 [0] | 2.075 [53] | 2.272 [44] |In the Kedify Dashboard, you can also observe the traffic load and resulting scaling:
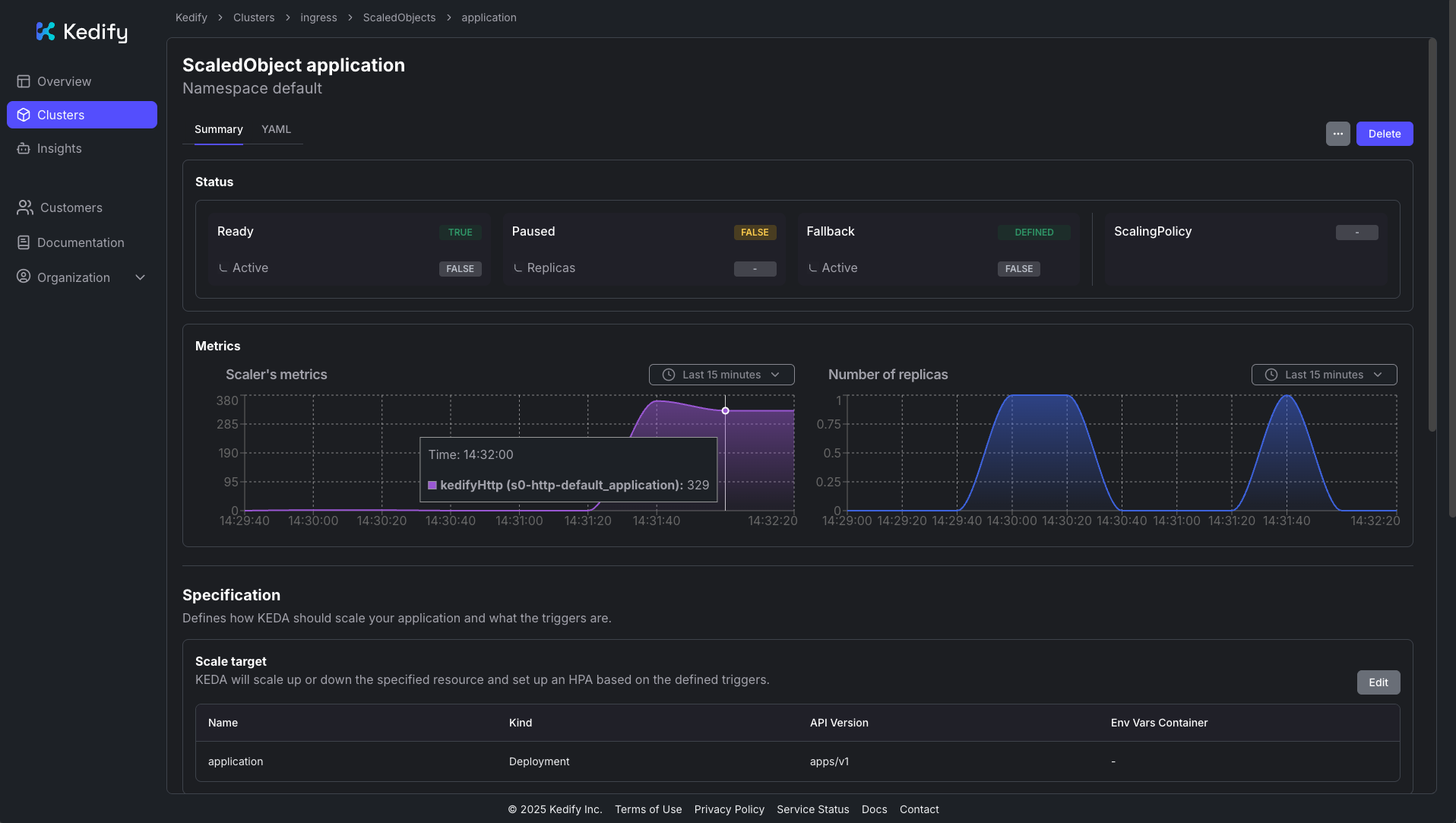
Next steps
Section titled “Next steps”You can explore the complete documentation of the HTTP Scaler for more advanced configurations, including other ingress types like Gateway API, Istio VirtualService, or OpenShift Routes.