HTTP Scaler (Inference)
HTTP Scaler ensures that your inference workloads scales based on incoming HTTP requests.
Details
Section titled “Details”The HTTP scaler is designed specifically for ScaledObject resources to enable scaling based on incoming HTTP traffic; for more information on regular workloads see the HTTP Scaler section. This page will cover usage for the HTTP scaler for inference workloads
Modern inference workloads deployments include usage of InferencePool, this is an object defined as part of the Gateway API Inference Extension which allows for users to select groups Inference-focused Pods and defines an Extension that allows selection of pod for each request. The extension is often referred as Endpoint Picker. InferencePool is very similar to a Service (a way to select Pods and specify a port).
The HTTP Scaler is capable of scaling inference workloads by referencing InferencePool. The InferencePool CRD spec, also contains a reference to know which Endpoint Picker to use. Endpoint Picker is a deployment that acts as a router by selecting the best backend for each request.
In the ever-growing landscape of LLM tools, the community seems to agree that vLLM solves many of the serving challenges for inference workloads. vLLM is a fast, open-source inference engine for LLMs that maximizes GPU utilization with techniques like PagedAttention, KV Cache aware routing, and Prefill/Decode Disaggregation.
vLLM is great at making a single GPU more efficient, but you still need to decide when to scale, how much to scale, and what metrics should trigger the autoscaling. It doesn’t solve autoscaling by itself
The HTTP Scaler can target the deployment of the inference workload, while also autowiring inference components that are necessary to have advanced features like InferencePool and Endpoint Picker.
Architecture
Section titled “Architecture”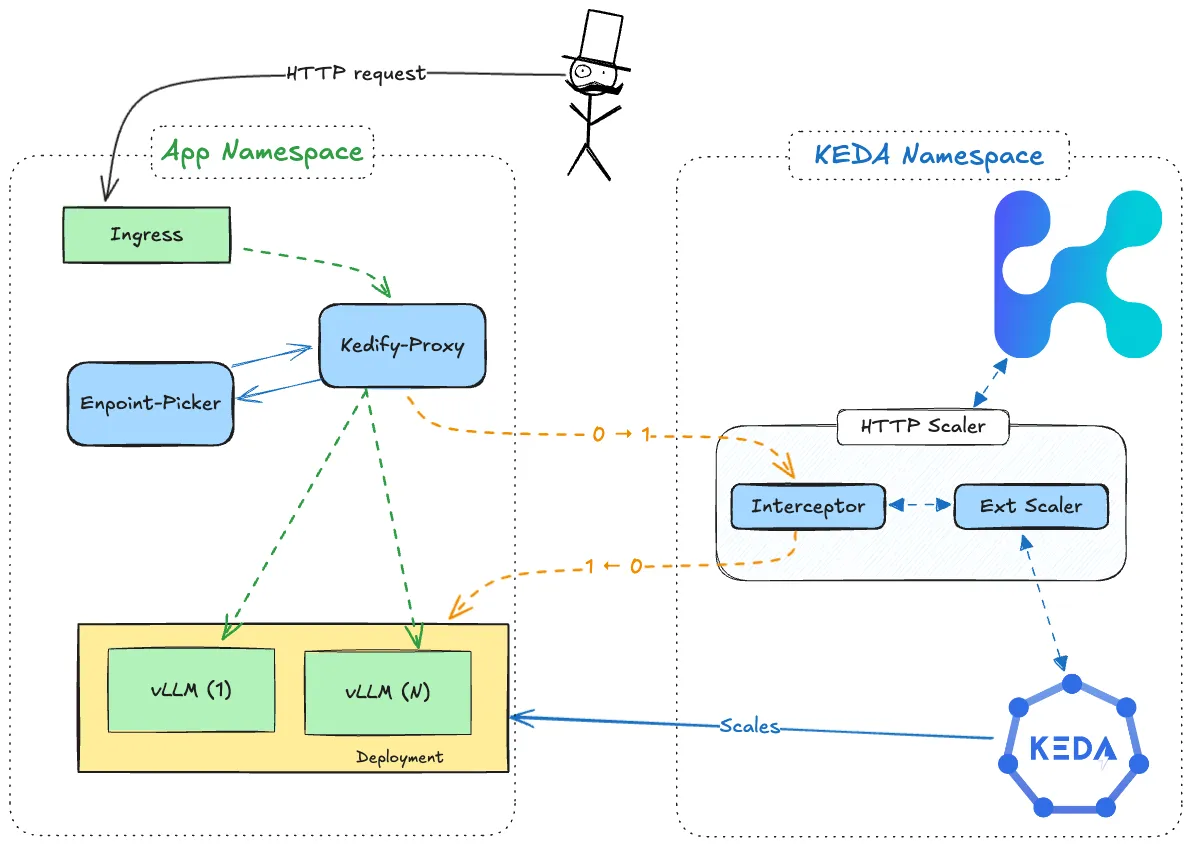
Trigger Specification
Section titled “Trigger Specification”This specification describes the kedify-http trigger, which scales inference workloads based on incoming HTTP traffic.
Here is an example of a trigger configuration using the HTTP scaler with an inferencepool:
triggers:- type: kedify-http metadata: hosts: application.keda pathPrefixes: /v1 service: vllm-llm-d-modelservice-inference-svc port: '9002' scalingMetric: requestRate targetValue: '5' granularity: 1s window: 1m trafficAutowire: ingress inferencePool: inferencepoolComplete parameter list:
Section titled “Complete parameter list:”A list of complete parameters can be found in HTTP Scaler section. Here we will contemplate the parameters related to inference workloads.
Routing configuration:
hosts: Comma-separated list of hosts to monitor (e.g.,www.my-app.com,www.foo.bar). This is used for routing the traffic to correct application and uses theHostheader for plaintext HTTP, SNI for TLS, and:authoritypseudo-header for HTTP/2. (Required)pathPrefixes: Comma-separated list of path prefixes to monitor, (e.g.,/foo,/bar, Optional, Default:/).headers: Structured list of HTTP headers to match for routing traffic. See more in dedicated section. (Optional)
Backend serving:
service: Name of the Kubernetes service for the workload specified inScaledObject.spec.scaleTargetRef, where traffic should be routed. Should be present for inference workloads to behave as expected.fallbackService: Name of the Kubernetes service used as a fallback along withserviceautowiring.port: Port on which the Kubernetes Service is listening. Only one ofportorportNamecan be set. For inference workloads the kedify-proxy listens on port 9002.portName: Reference to theportby its name. Only one ofportorportNamecan be set.tlsSecretName: Reference to aSecretcontaining the TLS certificate and key undercert.tls,key.tlsfor TLS reencrypt. Not necessary if using TLS termination at ingress and cluster internal traffic is plaintext or TLS passthrough (Optional).tlsMode: TLS mode for the traffic to the application, eitherplaintext,reencrypt,passthrough. If set toreencrypt, the TLS certificate and key must be provided in thetlsSecretNamefield. Thepassthroughmode is not compatible with any L7 routing options - path prefix or headers. (Optional)loadbalancing: Load balancing strategy used when proxying, supportsdns(default behavior, same as empty “or not defining any), oreds(envoy endpoint discovery service). See also dedicated section for more details. (Optional)
Inference Serving:
inferencePool: Name of the inferencepool containing a reference to an Endpoint Picker. The labels for the inferencepool should match the selectors from theservicedefined
Example ScaledObject with HTTP trigger and inferencePool
Section titled “Example ScaledObject with HTTP trigger and inferencePool”Here is a full example of a scaled object definition using the HTTP trigger:
kind: ScaledObjectapiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1metadata: name: inferencepool namespace: inferencepoolspec: scaleTargetRef: apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment name: vllm-llm-d-modelservice-decode cooldownPeriod: 600 minReplicaCount: 1 maxReplicaCount: 2 fallback: failureThreshold: 2 replicas: 1 advanced: restoreToOriginalReplicaCount: true horizontalPodAutoscalerConfig: behavior: scaleDown: stabilizationWindowSeconds: 600 triggers: - type: kedify-http metadata: hosts: application.keda pathPrefixes: /v1 service: vllm-llm-d-modelservice-inference-svc port: "9002" scalingMetric: requestRate targetValue: "5" granularity: 1s window: 1m trafficAutowire: ingress inferencePool: inferencepoolNote: Ensure that
hosts,pathPrefixes,service, andportparameters match the application’s routing requirements. Note: Ensure thatinferencePoolandserviceparameters use the same selectors.
Traffic Autowiring:
Section titled “Traffic Autowiring:”Kedify automatically re-wires ingress resources for the following implementations:
In a typical Kubernetes setup, the networking configuration is structured as follows:
Ingress -> Service -> Deployment
To enable automatic scaling based on incoming HTTP traffic, Kedify introduces additional components:
- kedify-proxy: An Envoy-based proxy that routes traffic and collects metrics for scaling.
- HTTP Add-on Interceptor: Ensures requests are routed and cached when the app is scaled to zero.
With Kedify, when the inferencePoolis referenced in the scaler spec, the traffic flow includes these additional components:
Ingress -> kedify-proxy -> ext_proc -> kedify-proxy -> Pods
For finer control over ingress resources autowiring, use trafficAutowire with a comma-separated list of resources to be autowired, including route for OpenShift Routes.
triggers: - type: kedify-http metadata: trafficAutowire: "httproute,ingress,virtualservice,route"Note: Traffic autowiring for inference workloads, uses the port 9002 on the kedify-proxy for inference traffic.
Autowiring Fallback
Section titled “Autowiring Fallback”In case of control plane issues with kedify-proxy or interceptor, Kedify rewires traffic back to the original flow:
Ingress -> Service -> Deployment
This fallback avoids outages and keeps the application accessible. By default, traffic is rewired if Kedify detects control plane issues for over 5 seconds. This duration can be configured using agent.autowire.healthcheckDebouncerPeriod on the Kedify Agent helm chart.
Disabling Traffic Autowiring
Section titled “Disabling Traffic Autowiring”To disable traffic autowiring, specify:
triggers: - type: kedify-http metadata: trafficAutowire: "false"In this case, users must manually wire the networking traffic. Note that Autowiring Fallback does not apply here.
Kedify Proxy
Section titled “Kedify Proxy”The Kedify HTTP Scaler uses the kedify-proxy (Envoy) to route traffic and collect metrics for applications, enhancing reliability and performance. This proxy setup helps prevent potential bottlenecks in the interceptor. Currently, Envoy is the only natively supported proxy for the HTTP Scaler; other reverse proxy solutions may require additional configuration.
Since kedify-proxy is based on envoy, we can make use of advanced features that enable integration with Gateway API inference Extension. We make use of the envoy feature external processing filters. ext_proc allows us to attach a filter to each http request so we can have a external entity processing the requests and selecting the best backend to forward the inference requests. This allows to have features like intelligent scheduling based on KV cache or Prefill-Decode disaggregation.
Deployment Options for Kedify Proxy
Section titled “Deployment Options for Kedify Proxy”There are two main deployment configurations for kedify-proxy: Namespace-Level and Cluster-Wide.
-
Namespace-Level Deployment (Default): By default,
kedify-proxyis deployed in each namespace that contains at least oneScaledObjectusing thekedify-httptrigger. This approach ensures that traffic routing and metric collection are confined within the namespace where theScaledObjectis defined, providing isolation and control. -
Cluster-Wide Deployment (Optional): For environments where Istio’s VirtualService is used (currently the only supported configuration),
kedify-proxycan be deployed cluster-wide. In this setup,kedify-proxyis deployed in the KEDA installation namespace and shared among allScaledObjectsacross namespaces. This configuration allows centralized traffic routing and scaling across all namespaces in the cluster.- To enable cluster-wide deployment, set the Kedify Agent helm chart option
kedifyProxy.clusterWidetotrueon the Kedify Agent. This will configure the Kedify Agent to deploy a single instance ofkedify-proxyfor the entire cluster, located in the KEDA installation namespace. For more details, refer to the Kedify Agent documentation.
- To enable cluster-wide deployment, set the Kedify Agent helm chart option
Note: The namespace-level setup for the
kedify-proxywhen enabledinferencepoolfor a scaler, will receive the traffic in port 9002.
Note: The cluster-wide setup for
kedify-proxyis only compatible with Istio’s VirtualService. Other types of ingress configurations are not supported in this setup.
Kedify Proxy Traffic Flow
Section titled “Kedify Proxy Traffic Flow”When using Kedify, the traffic flow in Kubernetes is enhanced to include additional components for real-time monitoring and scaling based on HTTP traffic. Typically, Kubernetes follows this traffic pattern:
Ingress -> Service -> Deployment
With Kedify serving inference workloads, the traffic flow includes kedify-proxy as an intermediary to monitor and intercept traffic before it reaches the service. Also the kedify proxy communicates with the external processor to decide which pods to forward the requests:
Ingress -> kedify-proxy -> ext_proc -> kedify-proxy -> Pods
The kedify-proxy intercepts, routes, and caches HTTP requests when necessary. This routing allows the scaler to collect traffic metrics and adjust replica counts based on real-time demands. For more details on autowiring and traffic routing configurations, refer to the Traffic Autowiring section.
External Processor
Section titled “External Processor”The external processor can be any service that implements the envoy ext_proc interfaces. Some common implementations for inference workloads are
- Gateway API Inference Extension Endpoint Picker (GAIE EPP)
- LLM-D Inference Scheduler
- vLLM Semantic Router
Scale-to-Zero for Inference Workloads
Section titled “Scale-to-Zero for Inference Workloads”The HTTP Scaler fully supports scale-to-zero for inference workloads. When traffic stops flowing to your inference endpoint, KEDA will scale your deployment down to zero replicas after the configured cooldownPeriod.
How It Works
Section titled “How It Works”- Metrics Collection: The
kedify-proxycollects RPS (requests per second) and Concurrency metrics for all inference traffic on port 9002 - Metric Aggregation: Metrics are pushed to the interceptor and forwarded to the scaler via gRPC bridge
- Scaler Reports to KEDA: The scaler receives metrics and reports them to KEDA
- Scaling Decision: KEDA uses these metrics to determine replica count, including scaling to zero when metrics reach zero
Enabling Scale-to-Zero
Section titled “Enabling Scale-to-Zero”To enable scale-to-zero for inference workloads, set minReplicaCount: 0 in your ScaledObject.
Using the example from HTTP Scaling for Ingress-Based Inference Workloads, change the minReplicaCount from 1 to 0:
kind: ScaledObjectapiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1metadata: name: inferencepool namespace: inferencepoolspec: scaleTargetRef: apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment name: vllm-llm-d-modelservice-decode cooldownPeriod: 600 minReplicaCount: 0 # Changed from 1 to enable scale-to-zero maxReplicaCount: 2 # ... rest of configuration from the how-to guideTip: For a complete working example including the inference scheduler (EPP) and model deployment, follow the HTTP Scaling for Ingress-Based Inference Workloads tutorial and modify
minReplicaCount: 0.
Traffic Handling During Scale-to-Zero
Section titled “Traffic Handling During Scale-to-Zero”When pods are scaled to zero, incoming requests are queued by the interceptor until pods become available. The traffic flow during cold start:
- Request arrives at
kedify-proxy(port 9002) - Interceptor detects no available pods and triggers scale-up
- Request is held until pods are ready
- Once ready, request flows through:
kedify-proxy -> ext_proc (EPP) -> kedify-proxy -> Pod
Note: Consider setting an appropriate
cooldownPeriodfor inference workloads. Inference models often have longer startup times, so a longer cooldown (e.g., 300-600 seconds) prevents unnecessary scaling oscillations.
Verifying Inference Metrics
Section titled “Verifying Inference Metrics”You can verify that metrics are being collected correctly for your inference workload using the following commands.
Check Current Metrics
Section titled “Check Current Metrics”Query the /queue endpoint to see real-time metrics:
kubectl get --raw /api/v1/namespaces/keda/services/keda-add-ons-http-interceptor-admin:9090/proxy/queueExample output:
{ "inferencepool/my-inference-hso": { "Concurrency": 5, "RPS": 42.5 }}The key format is namespace/httpscaledobject-name.
Understanding the Metrics
Section titled “Understanding the Metrics”| Metric | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| RPS | Requests per second (time-windowed average) | Use with scalingMetric: requestRate |
| Concurrency | Current number of active/pending requests | Use with scalingMetric: concurrency |
Testing with Traffic
Section titled “Testing with Traffic”Generate test traffic to verify metrics flow:
# Send 100 requests with 10 concurrent connectionshey -n 100 -c 10 -m POST \ -host "inference.example.com" \ -d '{"model": "my-model", "prompt": "test"}' \ http://localhost:9080/v1/completionsThen check the metrics:
kubectl get --raw /api/v1/namespaces/keda/services/keda-add-ons-http-interceptor-admin:9090/proxy/queue | jqMetrics Granularity
Section titled “Metrics Granularity”Metrics are aggregated per HTTPScaledObject, not per path or model. This means:
- All model requests (model-a, model-b) on the same HTTPScaledObject are combined
If you need to scale different models or paths independently, create separate HTTPScaledObjects for each.
Troubleshooting
Section titled “Troubleshooting”If metrics are not appearing:
-
Check the envoy-metrics-map: Verify the cluster-to-HSO mapping
Terminal window kubectl get --raw /api/v1/namespaces/keda/services/keda-add-ons-http-interceptor-admin:9090/proxy/envoy-metrics-map -
Verify kedify-proxy is running: Ensure the proxy is deployed in your namespace
Terminal window kubectl get pods -n <your-namespace> | grep kedify-proxy -
Check interceptor logs: Look for metrics-related messages
Terminal window kubectl logs -n keda -l app=keda-add-ons-http-interceptor -f